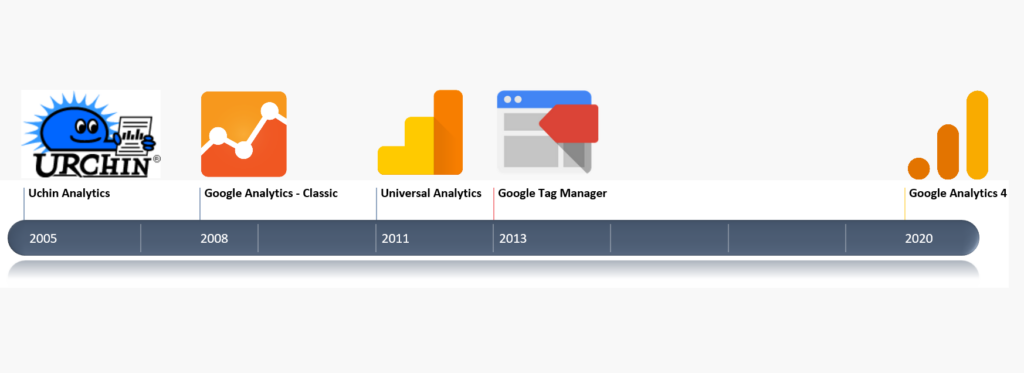
Google Analytics is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic. It was originally launched as “Urchin on Demand” in November 2005 by Urchin Software Corporation. Google later acquired Urchin in April 2005 and rebranded the software as Google Analytics. The initial version of Google Analytics was designed to track website traffic and generate reports based on the data.
Over the years, Google Analytics has undergone several major updates and changes. In 2007, Google introduced Google Analytics Premium, a paid version of the service that offered more advanced features and support for larger websites. In 2008, Google launched the Google Analytics Data Export API, which allowed developers to extract data from Google Analytics and use it in their own applications.
In 2011, Google released a major update to Google Analytics, called Universal Analytics. This version introduced several new features, including real-time analytics, multi-platform tracking, and improved customization options. It also introduced the Universal Analytics tracking code, which replaced the older ga.js tracking code.
In 2013, Google introduced Google Tag Manager, a tag management system that allows users to manage and deploy marketing and analytics tags on their websites. This made it easier for users to implement and manage Google Analytics and other marketing tags.
In 2020, Google announced the release of Google Analytics 4, the latest version of the service. Google Analytics 4 is built on a new data model that allows for more advanced tracking and analysis of user behavior across different devices and platforms. It also includes new features, such as machine learning-powered insights and enhanced privacy controls.
Overall, Google Analytics has evolved significantly since its inception in 2005, offering users increasingly advanced tools and capabilities for tracking and analyzing website traffic and user behavior.